Create dataset versions
In this guide
Overview
Create a new dataset version
Version constraints and relationships
Best practices for versioning
Overview
Create dataset versions to maintain a historical record of how published datasets evolve over time. Versioning creates a new draft dataset that is linked to the original through a version chain, allowing you to track the lineage and evolution of your data while the old version is automatically deprecated.
Create a new version when:
- You want to publish an updated dataset that supersedes an existing published version
- You want to maintain a historical record of dataset changes over time
- You want to ensure stakeholders are notified about newer versions of datasets they use
For example: Your organisation publishes Population Census 2020 and later releases updated data for 2025. By creating a new version instead of duplicating, you maintain a clear historical chain showing that Population Census 2025 supersedes Population Census 2020, and stakeholders are automatically notified about the newer dataset.
How versioning works:
- New versions can only be created from published datasets that don't already have newer versions.
- The new version maintains the same identifier as the previous version to ensure continuity.
- The new version starts as a draft with a link to its previous version.
- The original dataset is automatically deprecated when you publish the new version.
- The new version inherits all metadata from the previous version, including authentic source labels
Create a new dataset version
To create a dataset version, you must be a Catalogue Manager or have the permission to publish datasets. Check your permissions.
-
Go to the Published tab in the datasets panel.
-
Select the options icon ( ⋮ ) on the dataset you want to version.
-
Select Create a Version from the menu. The system creates a new draft version and opens the dataset editor.
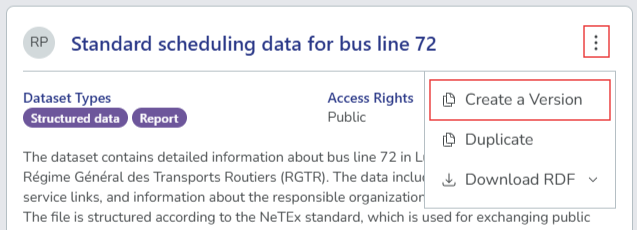
You can only create a new version from a published dataset that does not already have a newer version. If the dataset already has a newer version, the Create a Version button is disabled.
-
Update the new version with your changes:
- The title and other metadata are copied from the previous version
- All distributions and data dictionary entries are included
- Dataset relations and qualified attributions are preserved
- Authentic source assignments remain intact
- The status is set to Draft
-
Make your updates, then select Preview & Save to review your changes.
-
Select Save as Draft to save the new version. From here, you can continue editing, submit it for approval, and publish it. See: Dataset workflow.
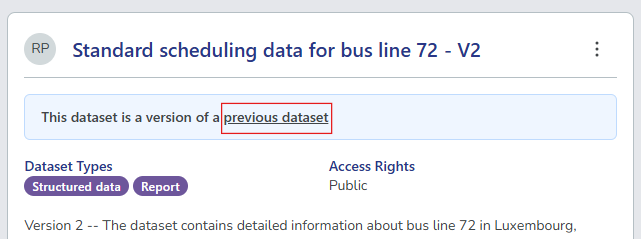
To view the previous version of the dataset, select the previous dataset link in the dataset card.
After publishing the new version, you can view the version history to see how the dataset has evolved over time.
Version constraints and relationships
Versioning follows specific rules to maintain clarity and consistency in dataset lineage:
- Same identifier: New versions retain the same identifier as the previous version to ensure continuity
- One active version: Only one version in a chain can be published without being deprecated
- Linear chain: Each dataset can have only one previous version and one next version
- No version of versions: You cannot create a version of a dataset that is already a newer version of another published dataset (wait until you publish the new version first)
What's included in the new version:
- All metadata fields: Title, description, temporal coverage, rights statement, etc.
- Distributions: Access URLs, formats, and all distribution metadata
- Data dictionary: Entries with authentic source assignments preserved
- Dataset relations: Links to other datasets or external resources
- Qualified attributions: Role assignments for organisations
What's not included in the new version:
- Activity logs (the new version starts with a fresh activity log)
- Comments (comments from the previous version are not copied)
- Status (the new version always starts as Draft)
- Approval and publication dates (these are set when the new version goes through the workflow)
Best practices for versioning
- Use clear version identifiers: Update the
versionfield (example: "1.0", "2.0", "2023", "2024") to make versions easily distinguishable - Add version notes: Use the
version_notesfield to document what changed in this version - Update temporal coverage: Adjust time periods to reflect the data covered by the new version
- Review all metadata: Ensure all metadata fields are current and accurate for the new version
- Verify data dictionaries: Check that field definitions remain relevant or update them as needed
- Test distributions: Ensure all distribution links and access methods work correctly
- Add comments during workflow: Use comments when submitting, approving, and publishing to document the versioning rationale